Project in brief
NGRA technology
NGRA strategy
RISK-HUNT3R impact
Project sustainability
Project in brief
Project in brief
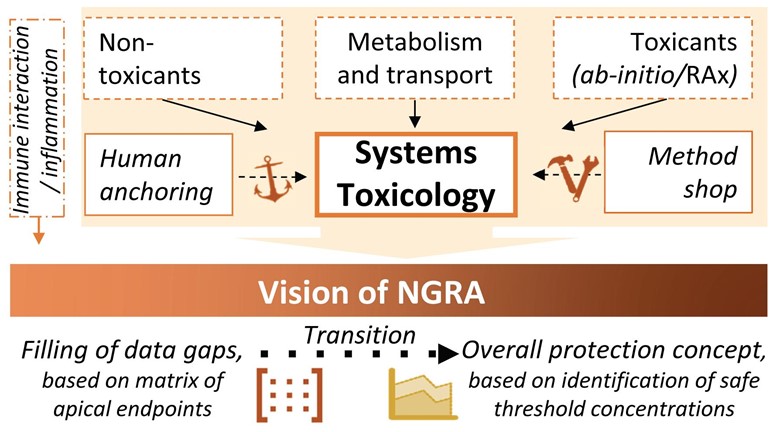
RISK-HUNT3R is the new European effort to develop a new modular framework for animal-free next generation risk assessment (NGRA) driven by world-leading experts from various disciplines.
The RISK-HUNT3R vision is to combine human exposure scenarios, in vitro hazard assessment, and NAM-based toxicokinetic and toxicodynamic testing, followed by integrative risk assessment via computational approaches and decision-making based on weight of evidence.
NGRA technology
NGRA technology
New approach methods (NAMs) in the context of RISK-HUNT3R are non-animal test methods, either in silico or in vitro. NAMs have become scientifically advanced in toxicology, allowing their broader application in chemical safety testing.
The RISK-HUNT3R testing toolbox is largely based on existing test systems of human origin that comply with a broad set of requirements to be used in risk assessment frameworks. Many in vitro systems are derived from pluripotent stem cells to ensure genome integrity. In addition, there are extensively investigated cell lines that are well known to have technical advantages for certain applications. Most test systems have been extensively documented in the EU-ToxRisk project as part of read-across case studies. New innovative test systems based on for example iPSC technology or organ-on-a-chip systems developed in other projects will require further assessment for implementation in safety testing scenarios, which RISK-HUNT3R will also spearhead.
NGRA strategy
NGRA strategy
The chemical safety testing toolbox will be implemented in a new risk assessment framework based on six interactive assessment modules:
- Problem formulation: define the mandatory risk assessment elements, the scope of the testing strategy (i.e., the required modules), and the overall acceptable uncertainty
- Assessment of human exposure and bioavailability
- Evaluation of metabolism, distribution, and excretion of chemicals
- Screening of effects in critical target organs
- Characterization of adverse effects and anchoring to human in vivo setting
- Data integration and uncertainty quantification for full risk assessment
RISK-HUNT3R impact
RISK-HUNT3R impact
Regulatory
The NAM-based NGRA strategy will provide a framework for chemical safety assessment that is truly human-centric.
RISK-HUNT3R will unite academic researchers, regulators, and safety scientists from industry to foster regulatory acceptance and direct practical application of NGRA in line with the Green Deal of the European commission.
NAM-based NGRA will find application in multiple regulatory contexts, across industry sectors, and in protecting different population groups, throughout all life stages, including the most vulnerable, children, pregnant women, and elderly.
Environmental
Toxicity testing is a prerequisite for reducing risks to humans and the environment. The RISK-HUNT3R NGRA framework will ensure faster and cost-effective early hazard and risk characterization of chemicals that will ultimately steer the restriction of use, replacement with safe alternatives or full production ban. This will ultimately reduce toxicant release to air, water and soil and thus minimize adverse impacts on human health and the environment.
Health
Due to the increasing life expectancy in the EU, exposure of citizens to chemicals may occur for many decades, and adverse effects may persist and evolve from childhood until old age. It is crucial to take action now and limit and manage human exposure levels to hazardous chemicals.
RISK-HUNT3R will directly relate case study compounds to exposome and biomonitoring studies through translational biomarkers, ensuring a direct translation to real-life exposure conditions. Predictions by these models will enable the understanding of acceptable exposure levels –including uncertainties– required to safeguard public health.
RISK-HUNT3R partners have strong involvement in past and present drug safety science projects, for instance from the European Innovative Medicine Initiative, and can translate findings to pharma ensuring the faster development of safer and more efficacious drugs, in particular when fast introduction of new drugs is critical for emergent situations (such as a pandemic).
Economical
RISK-HUNT3R will drive the development, production and marketing of safer chemical compounds in all sectors by reducing time and costs of validation and by accelerating the toxicity testing process. A major societal goal is to develop and push for regulatory acceptance of systems toxicology-based animal-free methods for chemical safety testing.
RISK-HUNT3R will ensure a faster decision on compound safety and market introduction, placing Europe at the forefront of the cell-based assay and screening market, and hence respond to the global need for safer innovative products.
Project sustainability
Project sustainability
The overall objective of the project is to create sustainability long beyond the runtime of the project. RISK-HUNT3R will make sure that all potential stakeholders will understand the advantages of NAM-based NGRA over current testing practices.
The goal is to ensure optimal conditions, in terms of regulatory and commercial objectives, for sustainable use of developed in vitro and in silico methods, and of testing strategies based on these NAMs.
For all relevant project outcomes, the RISK-HUNT3R sustainability plan includes the following actions:
- Overview of relevant NAMs, quality control, standardization, fit-for-purpose evaluation of method and project outputs, establishment of smart methods to support IATA application, assurance of cost and operational effectiveness to promote practical application, and establishment of an integrated commercialization platform for methods and strategies of animal-free safety assessment.
- Integration of all essential NGRA test methods in a commercialization strategy to steer the uptake in different industry sectors and impact on the efficacy and cost effectiveness of NAM-based chemicals safety assessment.